
LED Display Driver IC: Importance, Types And How To Choose
If you’ve ever wondered what makes LED displays so bright, sharp, and consistent, the answer lies in one small but crucial component — the LED display driver IC. Without it, the stunning visuals we take for granted on everything wouldn’t be possible.
In this article, we’ll break down what LED display driver ICs are, why they’re so important for display performance, and how to choose the right one.
Table of Contents
1. What Is an LED Display Driver IC?
An LED display driver IC is a small integrated circuit that manages how LEDs light up on a display. It’s a bridge between the display’s controller and the individual LED pixels. When a control system sends digital data — such as images or video signals — the driver IC converts that data into precise electrical outputs that each LED can understand.
In a typical LED screen, thousands of these chips are distributed across the modules. Each LED driver chip controls a specific group of LEDs, depending on the screen’s resolution and pixel density. The higher the pixel density, the more driver ICs are used to handle all the data signals.
Physically, the LED display driver IC sits on the printed circuit board of the LED module. It connects through data lines to the main controller, receiving constant streams of digital instructions. Once the data reaches the IC, it determines which LEDs should light up and when.
You won’t see the driver IC when you look at a display — it’s hidden behind the LEDs — but it’s what keeps the system organized. It translates digital commands into visible light patterns, making the screen capable of showing clear images, text, and motion.
2. Main Types of LED Driver Chips
There isn’t just one kind of LED driver IC — different displays use different types depending on their purpose, brightness, and level of precision.
2.1 Constant Current LED Driver IC
This is the most common type used in LED displays today. It keeps the electrical current stable for every LED, regardless of voltage fluctuations. That stability means each pixel stays the same brightness over time. It’s especially useful in high-resolution screens, where even tiny differences in brightness can ruin image consistency. Most fine-pitch and indoor LED video walls rely on constant current driver ICs for their uniform look and long lifespan.

2.2 PWM LED Driver IC (Pulse Width Modulation)
Instead of adjusting voltage or current directly, a PWM LED driver IC controls brightness by switching LEDs on and off very quickly — thousands of times per second. The ratio between “on” and “off” time defines how bright the LED appears. This method allows for smooth dimming, precise gray scale control, and higher color depth. Displays that need vibrant colors and soft brightness transitions often use PWM-based drivers.

2.3 Integrated or Smart LED Driver Chips
Newer LED technologies are moving toward “smart” or integrated driver ICs, where multiple functions — like current regulation, data decoding, and error detection — are combined into a single chip. This reduces PCB complexity and improves efficiency. Some advanced drivers even include feedback systems that detect faulty LEDs or correct color differences automatically.
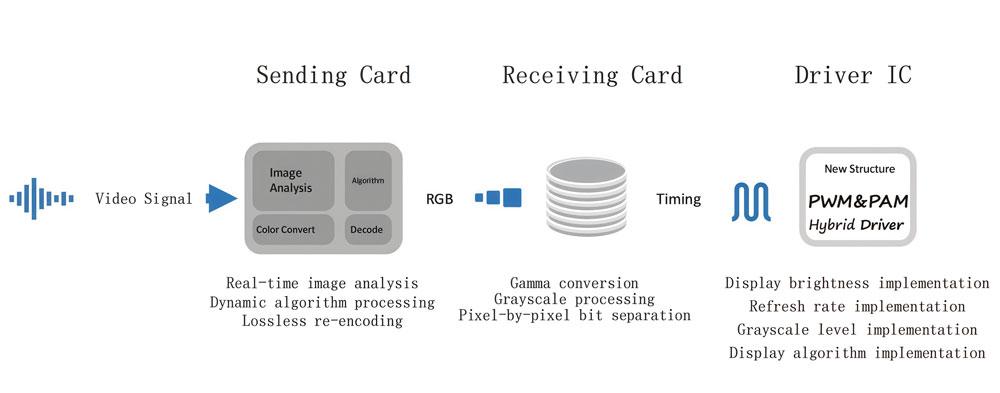
3. Why the Driver IC Matters in LED Displays?
The LED display driver IC is what turns a pile of LEDs into a real display. It’s the part that keeps the picture stable, the brightness even, and the motion smooth. Without it, modern LED screens — with their sharp visuals and high refresh rates — simply wouldn’t work the way we expect.
- Keeping Every Pixel in Line
On a large LED screen, millions of tiny LEDs light up together to form an image. The driver IC makes sure each one gets the exact signal it needs, at the right moment. It keeps the brightness and color balanced across the screen so the image looks clean and consistent instead of patchy or uneven.
- Making the Display More Reliable
LEDs are sensitive components. A small current fluctuation can make them flicker or fade over time. The LED driver chip regulates the electrical current going to every LED, preventing those issues and keeping the display stable even under heavy use. This steady control also helps extend the lifespan of the entire screen.
- Delivering Smooth Motion and High Refresh
If you’ve ever seen a display flicker or blur during fast-moving content, that’s usually a driver problem. High-performance LED driver ICs support higher refresh rates, meaning the screen updates more times per second. That’s what gives you smooth video playback, clean camera captures, and flicker-free visuals — even in broadcast environments.
- Enhancing Color and Depth
The better the LED driver IC, the more detail your screen can show. It can handle more steps of brightness, known as gray levels, which lets the display render deeper, richer color. The result is smoother gradients, more realistic tones, and an overall image that feels alive rather than flat.
4. How LED Driver ICs Work?
Every LED display works like a well-coordinated orchestra, and the LED display driver IC is the conductor. It doesn’t create the content — it makes sure every pixel lights up at the right time and in the right way.
At a basic level, the controller sends digital data — frames of an image or video — into the LED modules. The driver IC sits between the controller and the LEDs, translating that digital information into electrical signals. Each IC handles a specific number of LEDs, telling them when to turn on, how bright to glow, and how long to stay lit.
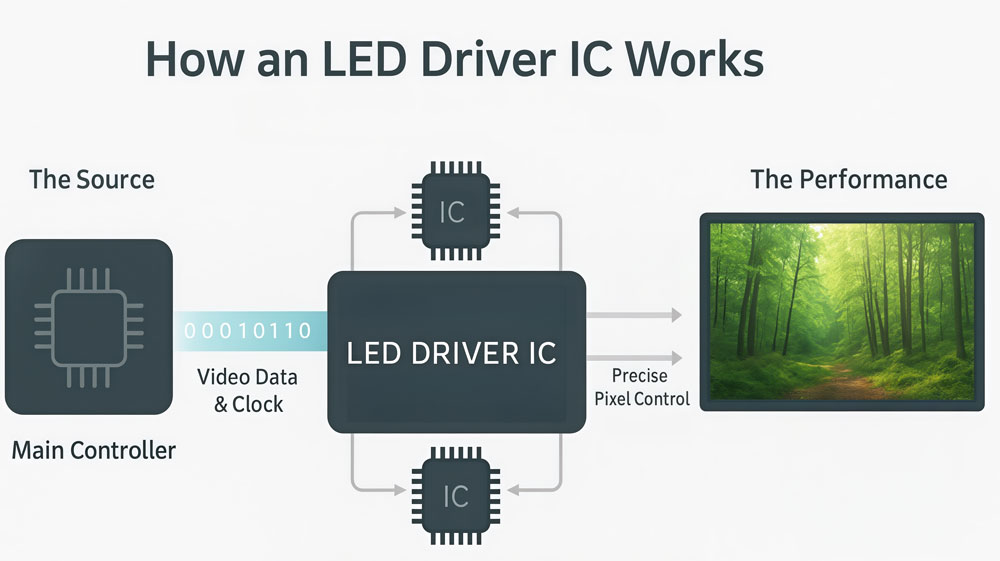
4.1 Signal Flow
Data moves through the system in a chain. The main controller pushes image data through the first driver IC, which passes it on to the next, and so on. This process happens extremely fast, frame after frame, so the display updates smoothly. The LED driver chip stores the incoming data for each LED until it’s time to refresh the image again.
4.2 Current Control
LEDs don’t like voltage changes. What they need is a stable current to shine consistently. The LED driver IC manages this — converting digital commands into constant electrical current for every pixel. That’s what keeps the screen uniform, with no flicker or uneven patches.
4.3 Timing and Synchronization
Each driver IC also synchronizes with others across the screen. It follows precise timing signals, making sure all LEDs refresh together. That’s how an entire wall of millions of LEDs can display one seamless, moving image without visible breaks or delays.
4.4 Behind the Scenes
All of this happens hundreds or even thousands of times per second. To the viewer, it just looks like a stable picture. But behind the scenes, the LED display driver ICs are constantly working — processing data, regulating current, and refreshing pixels — to keep every frame looking perfect.
5. Key Performance Metrics to Evaluate Quality
To understand what separates a good driver from an average one, you need to look at a few key performance metrics. These technical details are what define image quality, smoothness, and long-term stability.
① Refresh Rate
The refresh rate tells you how many times per second the display updates its image. A higher rate — usually 1920 Hz, 3840 Hz, or more — means smoother motion and no visible flicker. A strong LED driver IC keeps the refresh rate high, even with complex visuals or fine-pitch LEDs.

② Gray Scale and Color Depth
Gray scale is how many brightness levels each LED can show. The more levels it supports, the more natural and detailed the image looks. For example, a 16-bit driver IC can deliver over 65,000 brightness steps per color, giving smooth gradients and deep color transitions.
③ Channel Count and Integration
Each LED driver chip has multiple channels — usually 16, 24, or 32 — that control individual LEDs or groups. Fewer channels mean more chips are needed, which increases cost and complexity. Newer driver ICs integrate more channels in a single package, reducing the number of components on the board and improving efficiency.
④ Power Efficiency and Heat Control
LEDs consume constant power, and so does the driver IC. High-efficiency drivers use lower operating voltages, like 2.5 V instead of 3.3 V, and advanced semiconductor processes to cut down power loss. This not only saves energy but also reduces heat, which keeps the display stable and extends its lifespan.
⑤ Data Transmission Speed
Modern displays handle huge amounts of data per frame, especially at higher resolutions. A quality LED display driver IC must process and transmit that data fast — often above 30 MHz — to prevent delay or visual tearing. Faster transmission also helps maintain high refresh rates without losing synchronization.
6. How to Choose the Right LED Driver IC?
Choosing the right LED display driver IC isn’t just about price or brand — it’s about matching the chip’s performance to your display’s purpose. The right choice means better visuals, smoother motion, and a longer lifespan for the screen.
- Match the Application
Different environments place different demands on an LED screen, and your LED driver IC should fit those needs.
Indoor fine-pitch displays: Go for drivers with high gray scale performance, excellent color uniformity, and low power consumption.
Outdoor LED Screen or high-brightness screens: Choose high-current driver ICs that can handle larger currents and voltages. They deliver stronger brightness and are built to tolerate heat and weather changes.
Rental or stage LED screen: Focus on stability and refresh rate. Screens used for events and touring setups are constantly assembled and disassembled. You need driver ICs that stay reliable under frequent operation and perform well under cameras and stage lighting.

- Check Key Parameters
When comparing models, pay attention to the specifications that directly affect display performance:
Refresh rate: Look for 3840 Hz or higher for smooth, flicker-free video.
Gray scale: A 14-bit or 16-bit LED driver chip offers richer color and smoother gradients.
Operating voltage and power: Lower voltage means less heat and better energy efficiency.
Channel count: Fewer chips with more channels reduce cost and simplify the circuit.
- Consider Support and Compatibility
Even the best IC won’t help if it doesn’t work well with your control system. Always check compatibility with your LED controller cards, and make sure the manufacturer provides software tools, documentation, and long-term supply support. Reliable tech support can save you a lot of time during setup and maintenance.
For more insights into professional LED display systems and component selection, visit LedInCloud — your trusted LED Screen Cloud Platform for LED display technology and industry expertise.
7. Popular LED Driver Models
Different LED driver ICs support different refresh rates, which directly affect how smooth and stable a display looks. Below is a summary of several widely used models and their typical refresh performance.
| Driver IC Model | Typical Refresh Rate |
| SM16206 | 1920 Hz |
| SM16208 | 1920 Hz |
| SM16238 | 1920 Hz |
| SM16169 | 3840 Hz |
| SM16380 | 3840 Hz |
| SM16389 | 3840 Hz |
| ICND2037 | 1920 Hz |
| ICND2038 | 1920 Hz |
| ICND2046 | 1920 Hz |
| ICND2047 | 1920 Hz |
| ICND2150 | 3840 Hz |
| ICND2153 / ICND2153S | 3840 Hz |
| ICND2159 | 3840 Hz |
| ICND2163 / ICND2165 | 3840 Hz |
| ICND2055 / ICND2065 | 3840 Hz |
| ICND3065 / ICND3069 | 3840 Hz |
| MBI5124 | 1920 Hz |
| MBI5251 / MBI5253 / MBI5264 / MBI5754 | 3840 Hz |
8. Frequently Asked Questions
What’s the difference between a driver IC and a controller?
The controller handles image or video processing — it sends digital data to the display.
The LED driver IC is what turns that data into electrical signals for each LED.
You can think of the controller as the “brain” and the driver IC as the “muscle” that executes the command.
Does refresh rate really affect picture quality?
Yes. A higher refresh rate makes motion smoother and reduces flicker, especially when the display is filmed by a camera.
For professional video walls or broadcast screens, 3840 Hz or above is usually the standard.
How can I tell which driver IC my screen uses?
You can usually find the driver model printed on the LED module’s circuit board — it often starts with names like MBI, ICND, or SM.
If you’re unsure, check your screen’s specification sheet or contact the manufacturer for details.
Why do some screens flicker when filmed?
That’s a common sign of a low-refresh driver IC.
When the refresh rate is too low, the LED pulses become visible to the camera sensor, creating rolling lines or flicker.
Upgrading to a high-refresh driver IC (like the ICND2153 or MBI5253) solves this issue.
Do all LED driver chips work with every control system?
Not always. Some ICs are optimized for specific controllers or software.
When designing or upgrading a display, check for compatibility between your driver IC and the control system — otherwise, you might run into communication or color mismatch problems.
9. Conclusion
As LED technology continues to evolve toward higher resolution, faster refresh, and smarter integration, the role of the LED driver IC will only grow more important. Understanding how it works — and choosing the right one — is the first step to building displays that truly stand out.
If you’re planning your next LED display project and want to choose the right LED driver IC or learn more about compatible control systems, our team can help.
Contact LedInCloud today to discuss your project or explore technical options that match your needs.
