LED Display Receiving Card – The Brain Behind Every LED Screen
An LED display receiving card connects the control system to the LED screen. It receives image data, processes it, and sends precise signals to each LED module. Without this card, a display can’t show any picture.
This article explains how an LED receiving card works, what features matter in real use, and how to select one that fits your display setup.
Table of Contents
1. What Is an LED Display Receiving Card?
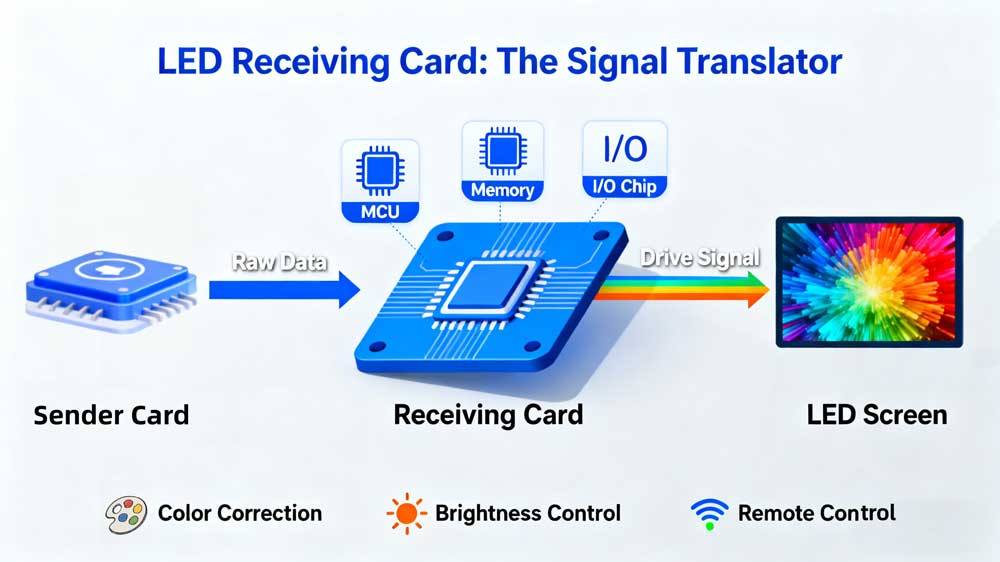
An LED screen receiving card is a small control board installed inside every LED cabinet. It gets data from the sending card or controller and translates it into signals that the LED modules can use.
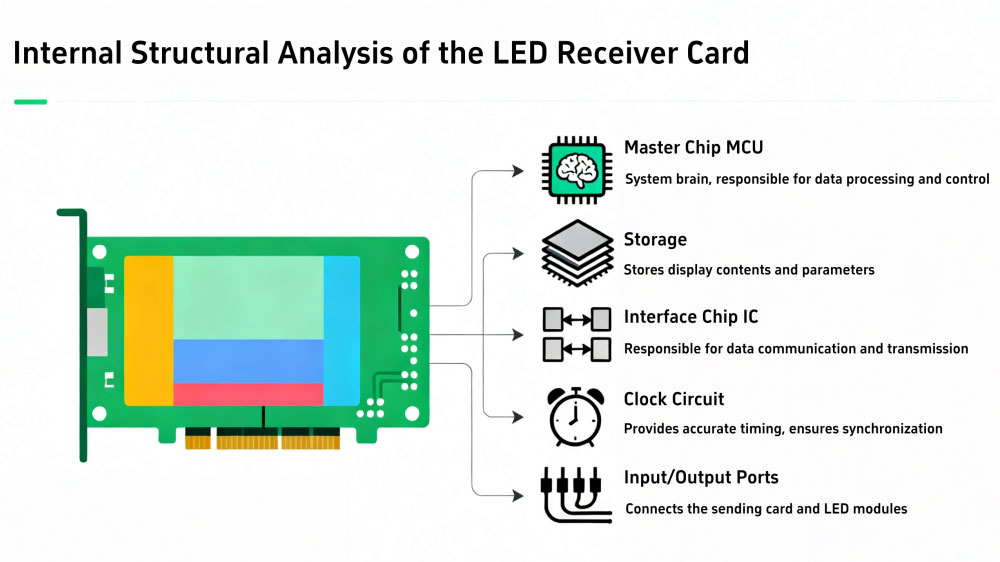
Each card contains:
- MCU (microcontroller) – handles data timing and logic.
- Memory – stores parameters and frame data.
- Interface chips – send signals to LED modules and communicate with the controller.
In simple terms, the card receives image data, organizes it into pixel information, and drives the LEDs to show that image. A large screen uses many LED receiver cards working in sync, each controlling one cabinet.
If you’re new to LED control systems and want to explore different display types, you can visit our LED Screen Cloud Platform to learn more about complete LED solutions and products.
2. Core Functions in an LED Screen System
A receiving card for LED display works as the bridge between image data and what appears on the screen. Every frame, color, and pixel depends on how it performs. Below are the main tasks it handles in a running LED system.
2.1 Data Reception
The LED display receiving card first takes image data from the sending card or main controller. This data travels through an Ethernet cable or optical fiber, depending on the system design. Each packet includes pixel information, brightness values, and timing details.
2.2 Data Decoding and Allocation
Once the card receives data, it splits and arranges it according to the LED panel layout. It decides which part of the image belongs to which module or cabinet. If a screen has many cards, each card only processes the section assigned to it.
2.3 Signal Conversion
After decoding, the receiving card converts the data into signals that match the driver ICs of the LED modules. Different modules use different drive chips, so the LED receiving card translates the generic video data into the exact pulse sequence those chips need. This process keeps pixel mapping accurate and avoids image distortion.
2.4 Brightness and Color Processing
The card also adjusts grayscale and color levels for each pixel. It calculates how much current each LED needs to reach the correct brightness and color tone.
Modern cards can handle high-bit grayscale, which allows smoother gradients and cleaner color transitions.
2.5 Synchronization
Every card works with the sending card in real time. If even one card runs out of sync, the display shows tearing or flicker.
To prevent this, receiver cards refresh their data continuously and stay aligned with the master timing signal from the controller.
2.6 Communication and Monitoring
Besides handling video data, the LED receiving card communicates status information back to the control software. It reports temperature, signal status, and voltage levels.
This feedback helps operators check system health without opening the cabinet.
In short, the receiving card for LED display manages the flow of data from the controller to every LED pixel. It receives, interprets, adjusts, and sends signals thousands of times per second. When all cards work together, the LED screen shows a single smooth image.
3. Key Features of a LED Screen Receiving Card
Different models and brands offer unique designs, but most good cards share the traits below.
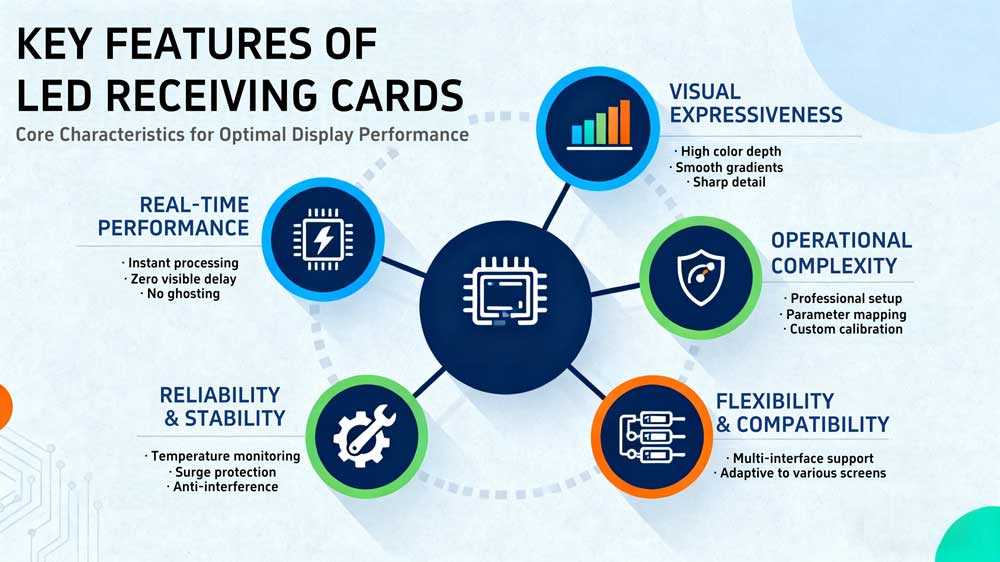
- Real-Time Performance
An LED display receiving card handles data instantly after it arrives. It processes each frame on the fly and sends it to the LED modules without visible delay.
Stable real-time behavior also reduces ghosting and motion lag, which can appear when the signal flow is slow.
- Visual Expressiveness
Display expressiveness refers to how well the card reproduces fine detail, color, and brightness.
High-quality cards support higher color depth and smoother grayscale transitions, which create a cleaner, more natural image. They maintain sharpness in high-resolution displays and avoid visible banding in gradients.
- Operational Complexity
Setting up an LED screen receiving card is not plug-and-play.
Each screen has its own pixel layout, scan mode, and wiring pattern. Configuring these parameters takes experience and accurate software mapping. Once done, the settings can be stored inside the card for reuse, but initial adjustment still requires technical skill.
- Reliability and Stability
An LED receiver card runs continuously inside an enclosed metal cabinet, often in heat and dust. It must stay stable under long-term operation.
Durable designs include temperature monitoring, surge protection, and secure signal connectors. Strong anti-interference performance prevents flicker or noise from nearby power lines. A reliable card keeps the screen operating for months or years with minimal downtime.
- Flexibility and Compatibility
A flexible LED receiver card supports multiple communication interfaces—Ethernet, serial, or sometimes wireless—and works with different control systems.
It can adapt to curved, floor, or transparent LED screen without changing the main controller.
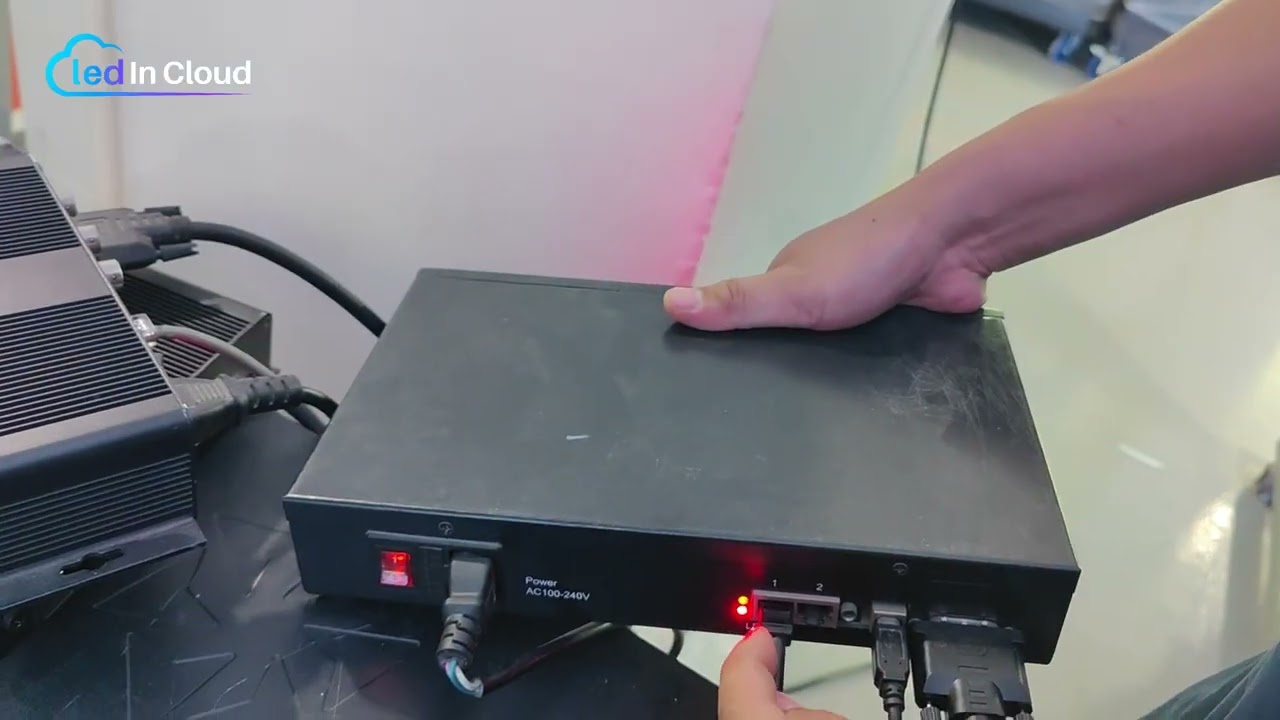
4. Installation and Connection Guide
A well-installed LED screen receiving card system not only improves performance but also prevents common problems such as flickering, loss of signal, or image delay during operation.
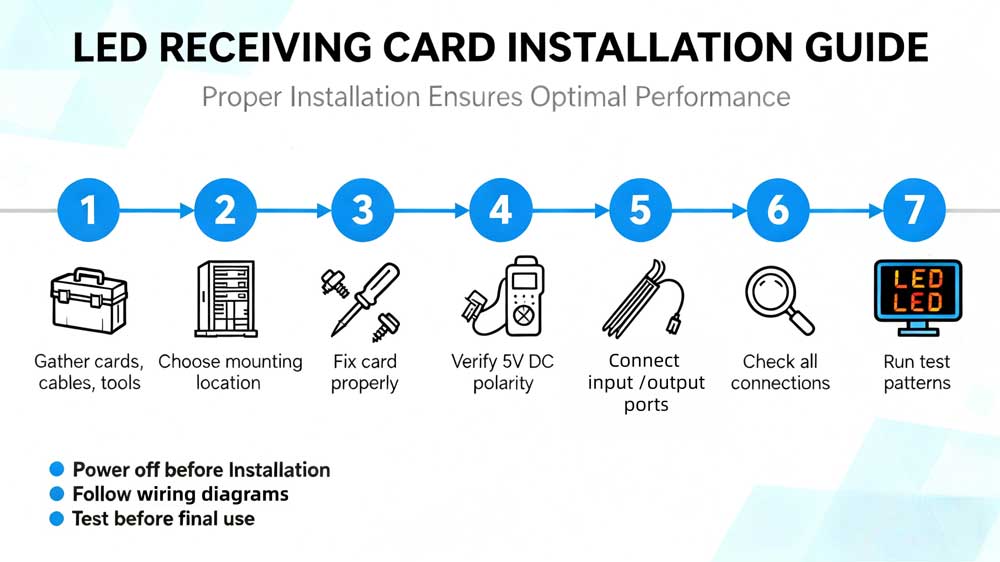
4.1 Installation Steps
- Step 1 — Prepare tools and parts.
Check that you have the LED display receiving cards, screws, screwdrivers, flat cables, network cables and a suitable power supply. Keep spare connectors and a multimeter on hand. Clear workspace around the cabinet to avoid losing small parts.
- Step 2 — Position the receiver card.
Choose a mounting spot inside the LED frame where cables can run cleanly and access is easy. Common locations are along the top or bottom inner edge of the cabinet. Leave enough room for the power connections and ribbon cable routing.
- Step 3 — Secure the card.
Mount the card with the correct screws or brackets so it does not shift during transport. Tighten fasteners to normal torque; avoid over-torquing plastic standoffs. Check that the card sits flat and the connectors line up with the cable paths.
- Step 4 — Connect power.
Hook the card to the cabinet power rail or dedicated 5V DC supply as specified by the manufacturer. Verify the polarity and the voltage rating before switching power on. Use proper fuses or breakers in the cabinet power chain.
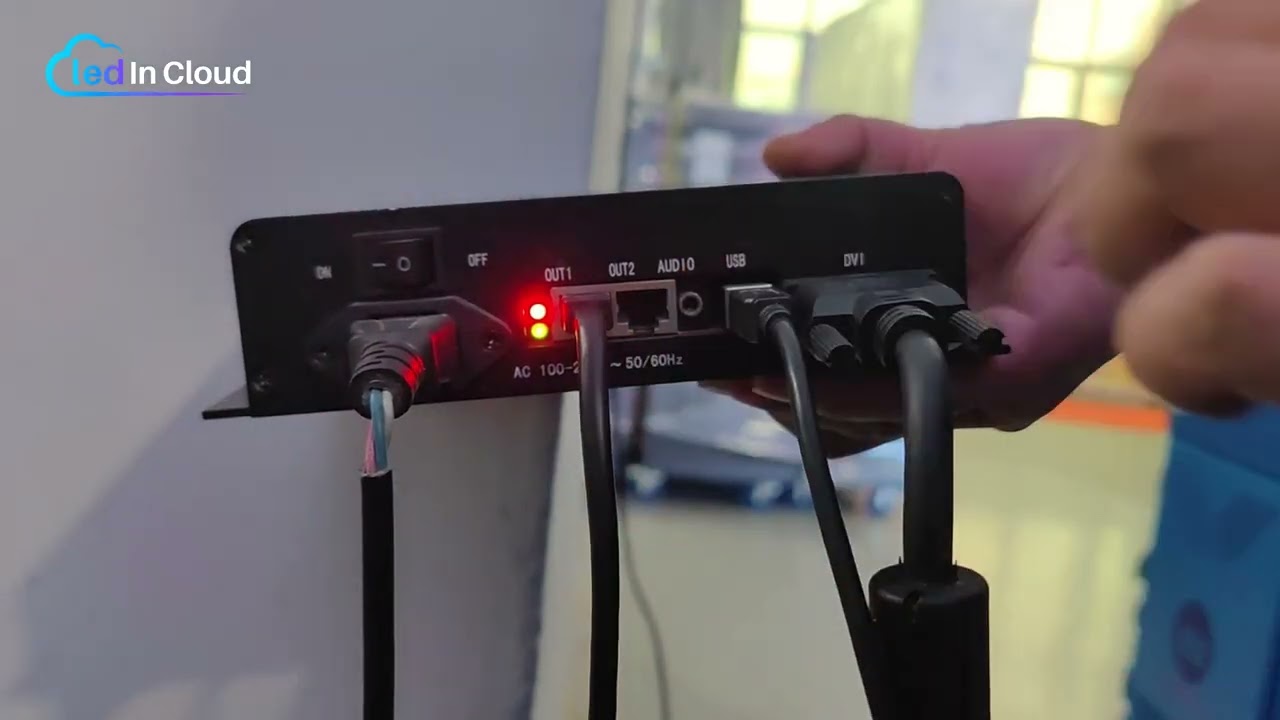
- Step 5 — Connect data lines.
Run the network cable from the sending card or controller to the LED receiving card’s input port. For chained cabinets, connect the OUT of one card to the IN of the next in sequence. Use correct flat ribbon cables from the card’s output ports to each LED module following the wiring diagram.
- Step 6 — Inspect all connections.
Before power-up, check that every connector is fully seated and screws are tightened. Look for damaged wires, exposed conductors, or misaligned plugs. If anything looks abnormal, replace the suspect part before testing.
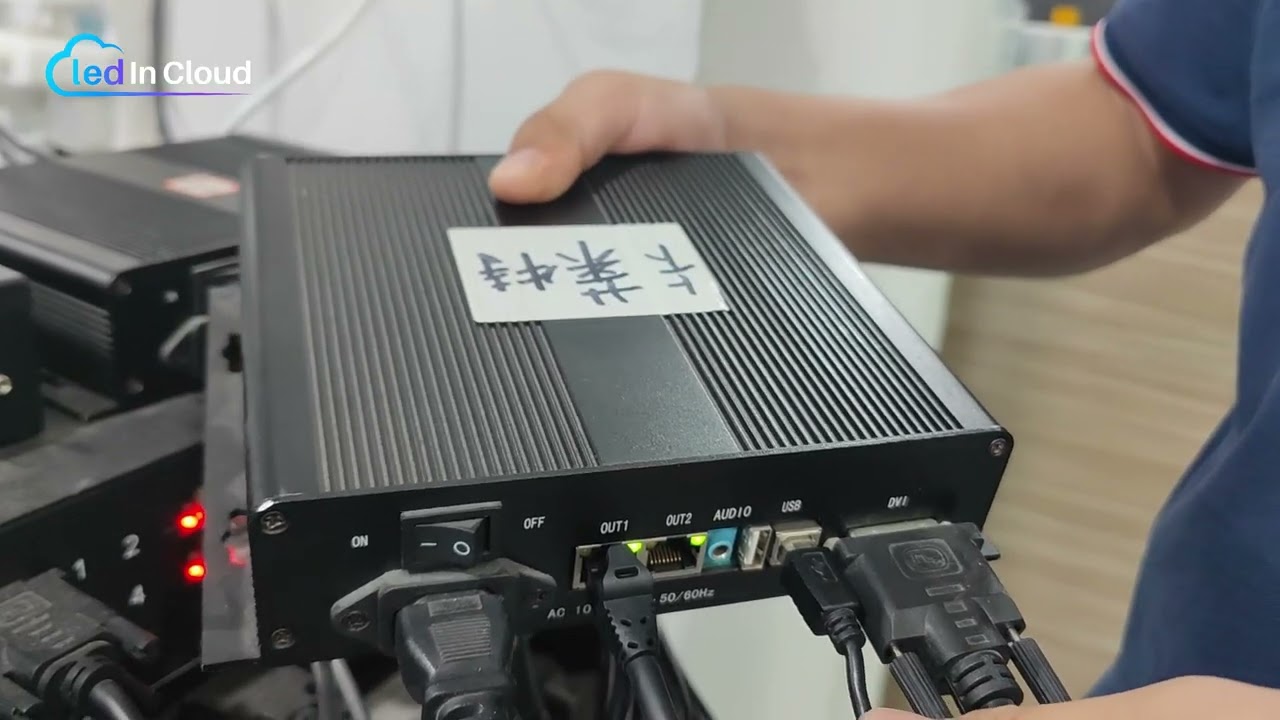
- Step 7 — Power up and test.
Turn on power and open the control software to verify card detection and communication. Run simple test patterns and color bars to confirm module mapping and signal integrity. If any section shows errors, shut down and recheck wiring and configuration.
4.2 Typical Installation Locations and Notes
Receiver cards are usually mounted inside the LED screen frame. The most common spots are the right side or the bottom inner edge of the cabinet. These positions make it easier to route flat cables and to access power and network ports during service.
Choose a location that keeps cables short and avoids tight bends. Short, neat cable runs reduce signal loss and make maintenance faster. Also leave space for airflow near the card; crowded wiring can trap heat and shorten component life.
Always follow the product manual for exact mounting points and connector orientation. If you swap card brands or module types, double-check wiring and pinouts before applying power. Keep a backup of the configuration file so a replacement card can be set up quickly if needed.
5. How to Choose the Right Receiving Card for LED Display?
Different LED display receiving cards vary in pixel capacity, control functions, and communication types. The right choice depends on your display’s size, resolution, and working environment. A well-matched card keeps the system stable and images consistent.
Compatibility
The card must match your LED display’s model, driver ICs, and control system. Different screens use different protocols and wiring patterns, so check both hardware and software compatibility. A properly matched card reduces setup problems and prevents data or mapping errors.
Performance
Choose a card with enough processing power and stability for your screen. Key indicators include data throughput, grayscale accuracy, and color correction. A capable card keeps motion smooth, colors accurate, and text clear—even in live or high-load conditions.
Interface and Communication
Select a card that uses the same communication method as your controller, such as Ethernet, optical fiber, or serial. The sending and receiving cards must share the same data protocol to maintain a stable signal. Fiber transmission is better for long-distance or interference-heavy setups.
Scalability
Pick a model that supports higher pixel loads, newer driver ICs, or larger resolutions. Scalable cards can be reused in future upgrades, saving cost and time during expansion.
Price and Value
Avoid low-cost cards that sacrifice stability or image quality. It’s better to choose a reliable, mid-range model that offers consistent performance and lower maintenance over time.
Brand Quality
NovaStar, Colorlight, Linsn, and Huidu offer solid build quality and regular firmware updates. Their cards integrate easily with common control systems and have reliable support.
Technical Support
Good support shortens downtime. Choose a brand that provides clear manuals, online tools, and responsive service. Timely help and firmware updates keep your display running smoothly.
Technical Support
6. Common Issues and Simple Fixes
Even well-built LED displays can face occasional problems during setup or operation. Most issues are easy to locate if you understand how the receiver card works. Here are some common cases and quick fixes.
(1) The display does not light up
If the screen stays dark after power-on, check the power supply first. Confirm that the receiving card for LED display is powered and the indicator lights are on. Inspect all flat cables and network connections for loose plugs or reversed data direction. If the sending card can’t detect the receiving card, try replacing the network cable or reloading the configuration file.
(2) Image shows wrong colors or reversed order
This often happens when the module wiring or scan type in the software does not match the physical screen. Open the control software and check the module parameters and color sequence (RGB order). Reload the correct configuration or swap the data cables according to the wiring diagram.
(3) Part of the screen flickers or shows random pixels
Flickering usually comes from poor contact, unstable power, or signal interference. Reseat the flat cables between the card and LED modules. Check grounding and make sure the power supply voltage is stable. If the problem appears only on one section, swap the module or LED display receiving card to see if the fault follows.
(4) Brightness or color inconsistency
Uneven brightness or color may result from incorrect calibration data or outdated firmware. Recalibrate the screen in the control software and update the receiving card firmware if available. Keep all cards on the same version to avoid mismatched processing.
(5) Configuration not saving or lost after restart
Some cards lose configuration when power is cut before the data is saved. After setup, click “Save to Hardware” in the software to write the configuration into the card’s flash memory. Avoid unplugging power during the process.
(6) Signal delay or low refresh rate
If images appear to lag or flash under camera, adjust the refresh rate and scan settings in the software. Use network cables with proper shielding and avoid excessive cable lengths. For high-frame-rate displays, upgrade to a card that supports a higher data bandwidth.
7. Conclusion
An LED receiving card may look small, but it carries most of the work that keeps an LED display running right. It controls how data moves, how color is rendered, and how every module stays in sync.
At LedInCloud, we work with well-known control systems such as NovaStar, Colorlight, and Linsn, and we help our customers choose the receiving cards that best fit their display needs.
If you need advice, configuration support, or a quote for your next LED project, feel free to contact LedInCloud — our team is here to help you find the best setup for your screen.