
LED Screen vs LCD Screen: Differences, Cost, and How to Choose
When people search for LED screen vs LCD screen, they want to understand the real difference.
Which one looks better? Which one fits their space?
This article breaks down the difference between LED and LCD screens in a practical way.
Table of Contents
1. What Is an LED Screen?
An LED screen is a display system that uses light-emitting diodes to create images directly. Each pixel consists of red, green, and blue LEDs. When these LEDs light up in different combinations, the screen forms the final image.
To understand LED screens clearly, it helps to look at two basic aspects: how they work and how they are built.

1.1 How an LED Screen Works
An LED screen generates light at the pixel level. Each LED emits its own light, rather than relying on an external light source. The control system adjusts the brightness of red, green, and blue LEDs to form colors and images.
Because the pixels emit light directly, the display can maintain stable visibility under different ambient lighting conditions. This working principle also allows precise control over brightness and contrast.
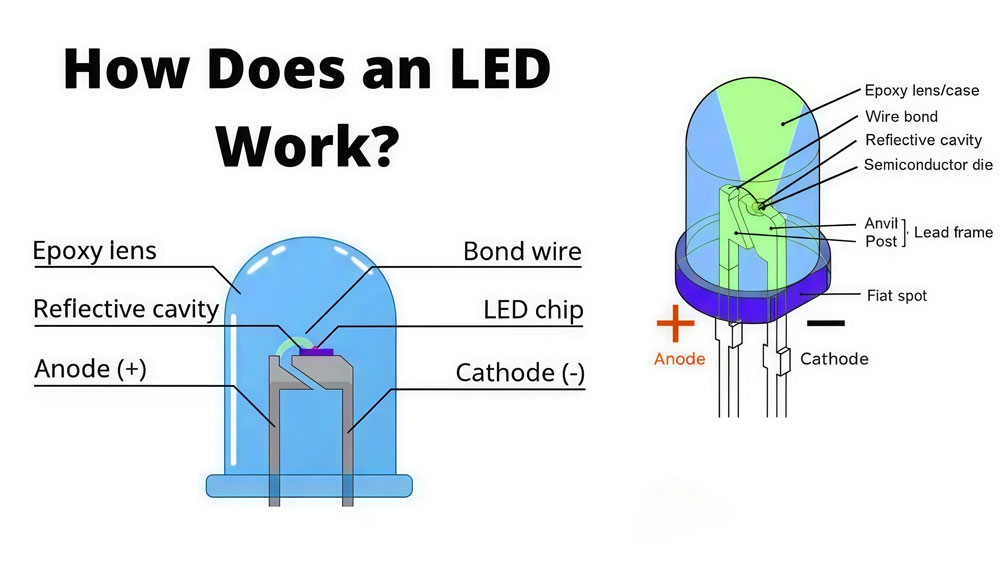
1.2 How an LED Screen Is Built
Manufacturers design LED screens as modular systems. Each module contains LED pixels, driving circuits, and control components. Installers assemble multiple modules together to form the final display surface.
This modular structure means the screen does not have a fixed size. Instead, the final dimensions depend on the number of modules used. Installers can adjust the screen size during installation to match project requirements.
2. What Is an LCD Screen?
An LCD screen is a display system that uses liquid crystal technology to control light transmission. LCD itself does not produce light. Instead, it relies on a separate light source to make images visible.

2.1 How an LCD Screen Works
An LCD screen controls light rather than generating it.
Inside the panel, liquid crystal molecules sit between layers of glass. When an electric current passes through these molecules, they change orientation and regulate how much light passes through.
Behind the liquid crystal layer, a backlight unit provides constant illumination. The LCD layer then shapes this light to form images. Color filters determine red, green, and blue subpixels, which together create full-color visuals.
Because LCD screens depend on a backlight, the brightness and contrast are influenced by the backlight system and panel design. This working principle defines how LCD displays handle light and color.

2.2 How an LCD Screen Is Built
Manufacturers build LCD screens as integrated panels with a fixed structure. The panel combines several layers, including the backlight unit, liquid crystal layer, color filters, and driving electronics.
Unlike modular display systems, an LCD screen has a predefined size and shape. The screen dimensions are set during manufacturing and cannot be adjusted after production.
This fixed structure makes LCD screens well suited for standardized display sizes, such as monitors, televisions, and professional flat panels. Once installed, the panel functions as a single, self-contained display unit.
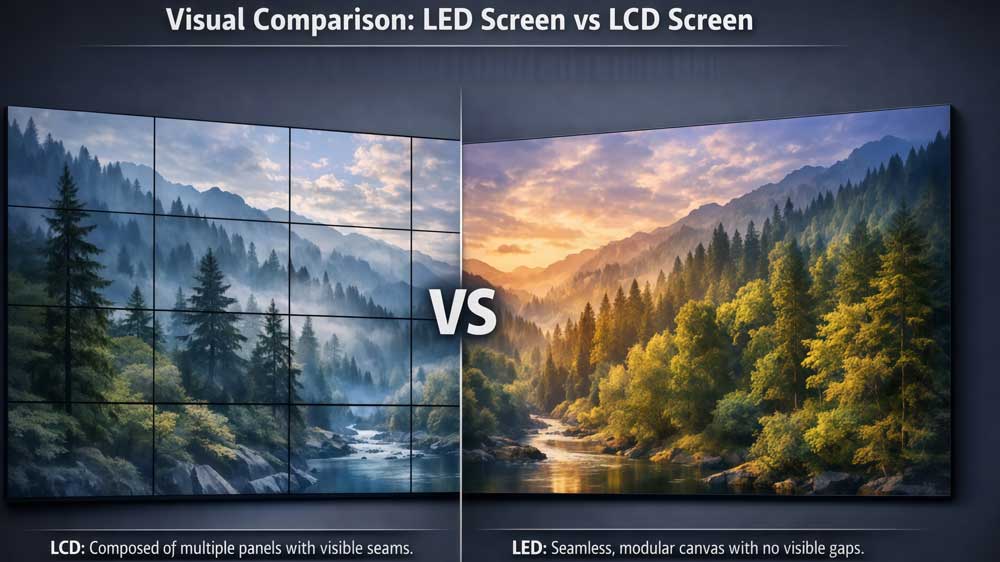
3. LED Screen vs LCD Screen: Key Differences
Once the basic working principles are clear, comparing an LED screen vs LCD screen becomes much more straightforward.
Although these two display technologies are often discussed together, their differences are structural and fundamental.
The table below summarizes the key differences between LED and LCD displays from a technical and practical perspective.
| Aspect | LED Screen | LCD Screen |
| Display technology | Direct-view LED display | Liquid crystal display with backlight |
| Light generation | Pixels emit light directly | Light comes from a backlight unit |
| Image formation | RGB LEDs form images at pixel level | Liquid crystals modulate transmitted light |
| Panel structure | Modular panels assembled on site | Integrated, factory-assembled panel |
| Screen size definition | Defined during installation | Defined during manufacturing |
| Scalability | Easy to scale by adding panels | Limited to available panel sizes |
| Seam structure | Visible pixel gaps depending on pitch | Continuous panel surface |
| Brightness control method | Individual pixel-level control | Backlight-level control |
| Viewing structure | Uniform brightness across modules | Brightness influenced by panel design |
| Installation logic | System-based installation | Mount-and-connect installation |
| System complexity | Multi-component display system | Single, self-contained display unit |
4. LED Screen vs LCD Screen: Pros and Cons
This section breaks down the pros and cons of LED screens and LCD screens based on actual usage conditions.

4.1 LED Screens
- Advantages
Better scalability for large displays
LED screens scale by adding panels. This makes LED screen solutions a better choice for large displays, where fixed LCD panel sizes quickly become a limitation.
Strong visibility in Outdoor
Because LED pixels emit light directly, LED screens handle high ambient light more effectively. This is why they are often used in environments where visibility matters more than fine detail.
Flexible system design
LED displays work as systems rather than single units. This allows flexibility in size, aspect ratio, and installation layout, which is difficult to achieve with standard LCD panels.
- Limitations
Higher entry cost for small sizes
For small display sizes, LED screens are usually more expensive than LCD screens. Even with a smaller screen, LED systems still require control hardware, power supplies, and installation work, which keeps costs relatively high.
Image uniformity depends on configuration
LED image quality depends on pixel pitch, calibration, and installation accuracy. If setup is not done properly, brightness and color may look uneven across the screen.
4.2 LCD Screens
- Advantages
Stable image quality in fixed sizes
LCD screens are produced as complete panels. Because the panel is manufactured and calibrated as a whole, image quality stays consistent across the entire screen.
More cost-effective at smaller sizes
For compact installations, LCD screens usually cost less. They deliver stable image performance without the need for separate control systems, cabinets, or complex assembly.
Simple and fast installation
LCD screens work as self-contained units. Installation mainly involves mounting the panel and connecting power and signal cables. There is no module alignment or system calibration.
- Limitations
Limited scalability
LCD panels come in fixed, predefined sizes. As the display gets larger, multiple panels must be combined. This often creates visible borders between panels, making the screen look like several displays joined together rather than one continuous screen.
Brightness constraints in bright environments
LCD screens use a backlight to display images. In very bright environments, the image can appear washed out if the backlight is not strong enough. Compared with LED screens, this makes LCD less suitable for outdoor or high-light locations.
5. LED Panel vs LCD Panel: Applications
After comparing performance and characteristics, the next question is practical: where does each display actually make sense to use?

5.1 Where LED Panels Are Commonly Used
LED panels are typically chosen for large-format displays and flexible installations.
They are widely used in:
- Outdoor advertising screens
- Building facades and media walls
- Stadiums and sports venues
- Large indoor venues such as exhibitions, halls, and event stages
- Control rooms or command centers requiring custom screen sizes
In these scenarios, screen size often exceeds standard panel dimensions. LED panels can be assembled freely, allowing the display to scale without visible borders. This makes them suitable for applications where continuity and size matter more than compact form.
Viewing distance also plays a role. Large LED displays are usually viewed from farther away, which reduces the impact of larger pixel pitch.
Large-format LED displays are widely used in outdoor advertising and public venues.
Many of these projects require custom sizing and system design, which is where LedInCloud – an LED Screen Cloud Platform provides tailored LED display solutions.
5.2 Where LCD Panels Are a Better Fit
LCD panels perform best in small to mid-sized displays with fixed dimensions.
Common applications include:
- Conference rooms and meeting spaces
- Retail signage and in-store displays
- Digital menu boards
- Monitoring stations and office environments
- Indoor information displays
In these cases, screen sizes are limited and well-defined. LCD panels provide consistent image quality right out of the box, without the need for complex system assembly. This makes them a practical choice when simplicity, cost control, and uniform image quality are priorities.
LCD panels are also often viewed at close range, where fine detail and pixel density are more noticeable.
6. LED Display vs LCD Display: Price and Cost
Price is one of the most common questions in the LED display vs LCD display comparison. However, cost is not just about the screen itself. Size, structure, and installation all play a role.
| Cost Aspect | LED Display | LCD Display |
| Initial screen cost | Higher at small sizes due to system components | Lower for small and mid-sized panels |
| Cost behavior as size increases | Scales more efficiently for large displays | Rises quickly as more panels are required |
| System components | Requires modules, control system, power supplies, and structure | Panel is integrated with backlight and electronics |
| Installation cost | Higher, depends on assembly and calibration work | Lower, simple mounting and connection |
| Maintenance approach | Modular replacement of individual parts | Panel-level replacement |
| Long-term cost impact | Can be lower for large screens over time | Predictable for small installations |
6.1 Initial Cost Differences
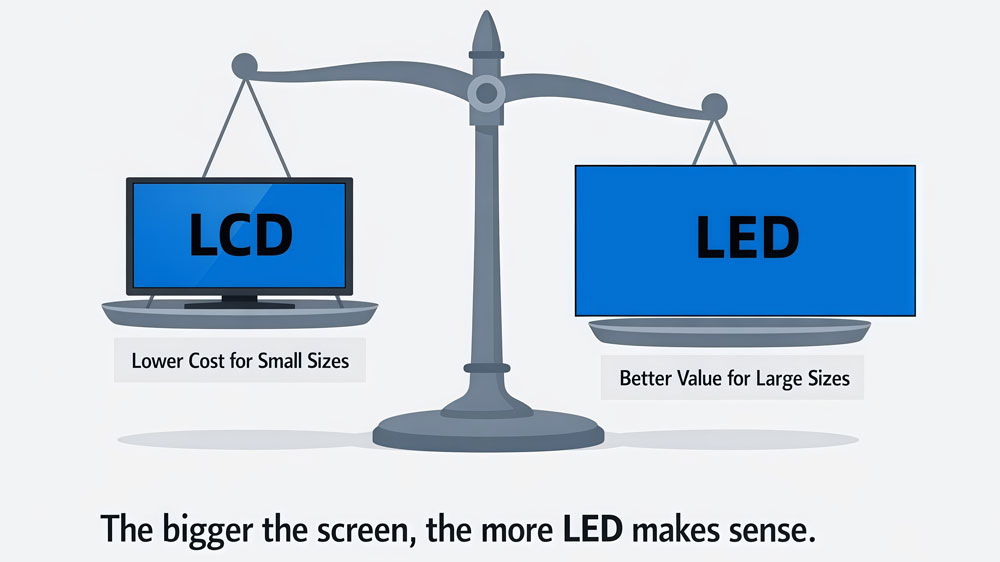
At first glance, LCD screens usually cost less than LED screens. This is especially true for small and mid-sized displays.
LCD panels are mass-produced as finished products. The price is clear, and the system is already integrated. When comparing LCD display vs LED display at smaller sizes, LCD often has a lower upfront cost.
LED screens work differently. Even a small LED screen requires modules, control systems, power supplies, and structural support. These components keep the initial investment higher.
6.2 How Screen Size Affects Cost
Screen size changes the comparison.
As the display gets larger, LCD costs rise quickly. Multiple panels are needed, along with mounting structures and alignment work. This increases both material and labor costs.
LED screens scale more efficiently at large sizes. Adding more modules increases size without changing the basic system design. This is why, for large installations, the price difference between LED and LCD display becomes much smaller.
In some large-format projects, LED can even be the more practical option.
6.3 Installation and Supporting Costs
Installation is often overlooked when comparing LED screen vs LCD screen cost.
LCD installation is usually straightforward. Panels are mounted, then connected to power and signal. Labor time is relatively short.
LED installation takes more effort. Modules must be assembled, aligned, and calibrated. The supporting structure and control system also add to the overall cost.
Because of this, installation expenses can vary widely for LED displays depending on project complexity.
6.4 Maintenance and Long-Term Cost
Long-term cost is not always obvious at the start.
LCD panels are typically replaced as whole units when issues occur. For small installations, this keeps maintenance simple.
LED screens are modular. Individual modules or components can be serviced or replaced without removing the entire screen. Over time, this flexibility can reduce downtime and maintenance impact, especially for large displays.
6.5 Cost Depends on the Project, Not Just the Technology
When people compare LED display and LCD display prices, they often expect a fixed answer. In reality, cost depends on how the screen is used, how large it is, and how it is installed.
7. How to Choose Between LED and LCD Screens?
When comparing LED screen vs LCD screen, the decision usually comes down to a few practical factors.
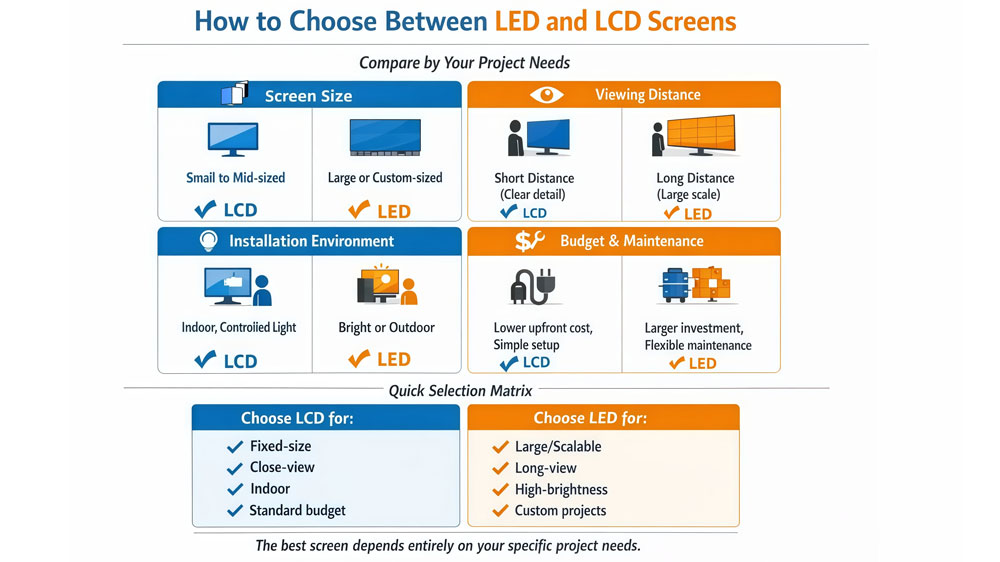
- Screen Size
- Small to mid-sized displays → LCD is usually the better fit
- Large or custom-sized displays → LED is more suitable
Screen size alone already answers many LCD vs LED display questions.
- Viewing Distance
- Short viewing distance → LCD offers clearer detail
- Long viewing distance → LED works well at larger scale
This explains why LCD compared to LED often looks better in close-up indoor use.
- Installation Environment
- Bright or outdoor environments → LED maintains better visibility
- Indoor, controlled lighting → LCD performs reliably
This is a common point in display technology LCD vs LED comparisons.
- Budget and Maintenance
- Lower upfront cost, simple setup → LCD
- Larger investment with flexible maintenance → LED
For small projects, LCD display vs LED display usually favors LCD.
For large projects, the cost difference becomes less obvious.
- Quick Summary
- Choose LCD for fixed-size, close-view, indoor displays
- Choose LED for large, scalable, high-visibility displays
This is why the question which screen is better LCD or LED only makes sense when tied to a specific project.
8. Conclusion
The comparison between LED screen vs LCD screen is not about choosing a “better” technology. It is about choosing the right display for the right application.
LED screens and LCD screens are designed for different use cases. LED displays are commonly used for large, scalable, and high-visibility installations. LCD displays are better suited for fixed-size, close-view, indoor environments where consistency and simplicity matter.
If you are still unsure which option fits your project, professional input can help avoid unnecessary cost and design issues.
Contact LedInCloud to discuss your display requirements. Our team can help you evaluate whether an LED display or LCD display is the better match for your specific application and budget.
